( For the texts and pictures books, publications, guidelines for example in awmf.org and contributions of colleagues were consulted.)
Melanoma
The term “tumor”, which is often mistakenly equated with “cancer” means “swelling-mass” and says nothing about whether a lesion is benign or malignant. Malignant melanoma originates from the pigment-producing cells (melanocytes). It is the most malignant of all skin cancers.
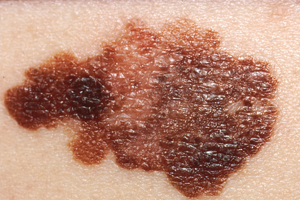
 Melanoma is not only growing rapidly, but often leads to early metastasis. Malignant melanoma is responsible for over 90% of deaths caused by skin cancer. Malignant melanomas occur only in 30% out of moles and in 70% of cases they arise new, on clinically healthy skin. It can also occur in scalp, mouth, gastrointestinal, eye. The major risk factors are brighter skin type, sunburns in youth, many atypical moles, melanoma in the family. Clinically suspicious signs of melanoma are: Change of shape, color, size of lesion Asymmetry or irregular boundaries of a mole Bleeding or crust Change of color or appearance of multiple colors within a mole Diameter of the area of more than six millimeters We recommend that people who have an increased risk of melanoma or already had a malignant melanoma, to investigate their skin at regular intervals (at least annually) by a dermatologist.
Melanoma is not only growing rapidly, but often leads to early metastasis. Malignant melanoma is responsible for over 90% of deaths caused by skin cancer. Malignant melanomas occur only in 30% out of moles and in 70% of cases they arise new, on clinically healthy skin. It can also occur in scalp, mouth, gastrointestinal, eye. The major risk factors are brighter skin type, sunburns in youth, many atypical moles, melanoma in the family. Clinically suspicious signs of melanoma are: Change of shape, color, size of lesion Asymmetry or irregular boundaries of a mole Bleeding or crust Change of color or appearance of multiple colors within a mole Diameter of the area of more than six millimeters We recommend that people who have an increased risk of melanoma or already had a malignant melanoma, to investigate their skin at regular intervals (at least annually) by a dermatologist.
Treatment
The surgical treatment is the most appropriate. Depending on the stage further treatment (sentinel lymphnode biopsy, immun-, chemotherapy, paliative care, radiotherapy) should be discussed.
