( For the texts and pictures books, publications, guidelines for example in awmf.org and contributions of colleagues were consulted.)
According to the recommendations and guidelines of the DGE:
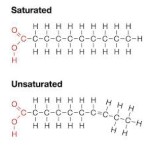
Fats are the most important energy suppliers. In addition, they perform many important functions in the human body. Saturated fatty acids are characterized chemically by the fact that there are no double bonds between the carbon atoms, whereas unsaturated fatty acids have multiple double bonds. Depending on how many double bonds are, a distinction is made between simple and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Image according to biochemistry books.
There are fatty acids that are essential to life, but can not be formed by the body itself. Therefore, they are also known as essential fatty acids. One of the essential unsaturated fatty acids include, for example, linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid, which belong to the omega fatty acids.
In addition to its role as an energy supplier dietary fats also ensure that the vital fat-soluble vitamins A, D , E, K can be absorbed by the body.
As part of a healthy diet, you should attach importance to the intake of unsaturated fatty acids. Unsaturated fats are found in particular in plant products such as olive oil, canola oil, safflower oil or linseed oil.
In foods containing animal fats, such as meat, lard, milk and butter, it is hard to find unsaturated fatty acids.
In addition, you should make sure that a sufficient amount is taken in essential fatty acids such as linoleic acid and alpha -linolenic acid because the body needs them but can not produce by itself. Products with a high content of essential fatty acids are, for example, vegetable oils. Sunflower oil, soybean oil or corn oil are rich in linoleic acid. In walnut oil or canola oil much alpha-linolenic acid is included. Essential fatty acids is attributed to a protective effect on the arterial vascular system. In addition, they should have a positive impact on the skin for chronic skin diseases such as psoriasis or eczema (atopic dermatitis) have.
Unsaturated and essential fatty acids !
Trans – fatty acids are formed during the industrial processing – in the partial hardening – of fats and oils that are rich in unsaturated fatty acids. Foods that contain hydrogenated fats – eg puff pastry, fried foods, potato chips or other snack items – often contain trans fatty acids. In small amounts, these fatty acids are also naturally in butter or milk.
Trans fats raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL -cholesterol in the blood. Because they increase the need for unsaturated fatty acids, trans fatty acids should provide less than 1 % of the energy. Foods that are rich in these fatty acids should be consumed rarely.
Tips for dealing with fats
Take a day not more than 68 to 80 grams of fat.
Take care, for example, hidden fats in meats, cheeses, pastries, snacks and chocolate. Choose low-fat cooking methods such as in the oven with baking sheet in the clay pot, in wok or specially coated pans.
For roasting a small spoonful of oil is enough, spread the oil with a brush in the pan. Simmer the food instead of frying them, if you add a little water before heating, the oil is not too hot. Be sure to use fats with a high proportion of unsaturated fatty acids, which are especially cold pressed vegetable oils such as sunflower seed, rapeseed, sesame oil or linseed oil.
Enrich the low-fat prepared foods just before eating with a spoon of this valuable plant oils, instead of admitting much fat already during the preparation.
Low-fat alternatives to mayonnaise for example, are Yogurt, cottage cheese or sour cream.
Fat burning
During physical exertion, the first energy is consumed from carbohydrates, then the energy comes from the fat deposits, but this occurs after about 30 minutes of continuous exercise. The fat burning is activated at this especially with lighter endurance exercise, because the more intense the physical activity, the greater the energy coverage by the faster- usable carbohydrates. For those who want to get rid of annoying fat reserves through sport, so is true: At least moderate training for half-hour without interruption, after that the extra weight goes on the collar!
Daily Value
The daily requirement of fat depends on the personal total energy requirement of a person. The total energy requirement varies depending on the age, body weight, physical work capacity and outdoor temperature.
About 25 to 30 percent of total energy intake should be covered by fats. Only certain groups of people, such as heavy laborers or athletes, the need for up to 40 percent. Children and young people have a higher fat requirement, which is between 35 and 40 percent depending on age. The average fat intake is far above the recommended requirements.
Fat composition
As part of a healthy diet not only fat intake plays a role. Rather, the proper weighting of different types of fatty acid is of importance. The ratio of unsaturated to saturated fatty acids should be approximately 2:1. Unsaturated fatty acids are included in particular in plant products, such as olive oil, while the fats of animal origin contain mainly saturated fatty acids.
Fats with a high content of the essential fatty acids linoleic acid and alpha -linolenic acid to be preferred. Every day should you take with food 2-7 grams of linoleic acid and 0.8 to 1.1 grams of alpha-linolenic acid to himself. Sunflower oil, soybean oil or corn oil are rich in linoleic acid, in walnut oil or canola oil much alpha-linolenic acid is included.
What foods are rich in omega -3 fatty acids, how much do we need?
The polyunsaturated omega -3 fatty acids, and n- 3 fatty acids called (for example, α – linolenic acid), lower triglyceride levels, improve the flow properties of the blood and thus prevent deposits in the blood vessels. They also affect the immune system and inhibit inflammatory reactions in the body. Good sources of n-3 fatty acids are canola and walnut oil, soybean oil and linseed oil. Longer-chain n-3 fatty acids (eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid) are mainly found in oily fish such as herring, mackerel and salmon.
The reference value for α -linolenic acid is 0.5 % of the total energy intake. Adults can reach (1-1.5 tablespoons) with about 10 to 17.5 g of this rapeseed oil. A serving of fatty fish (70 g) should be on the menu once a week.
Which fats are suitable for roasting and frying food ?
For roasting are suitable in principle all fats and oils. As part of the minimization of acrylamide formation in starchy foods such as potatoes or potato pancakes is currently recommended the use of margarine. For frying all oils and fats are suitable, which have a high content of monounsaturated fatty acids, such as olive oil or high oleic sunflower oil. In general, the fats and oils should have a low content of saturated and highly unsaturated fatty acids such as linolenic acid, because their susceptibility to oxidation is very large. The frying temperature should not exceed 175°C.
The fryer only at 60-80°C for 10 minutes to heat up the fat to melt, and only then to max. set up 175°C. Characterized local overheating and premature oxidative fat degradation is prevented.
The ratio of deep-fried to fat should be 1:10 to max. 1:15, ie, 100 g fried be 1-1.5 liters of fat or oil is needed.
To reduce the formation of acrylamide during frying of potatoes from raw potato slices, potato pancakes, etc. put margarine or oil with some margarine in a frying pan (at least 80 % fat). Generally fried potatoes should be made out of boiled potatoes.